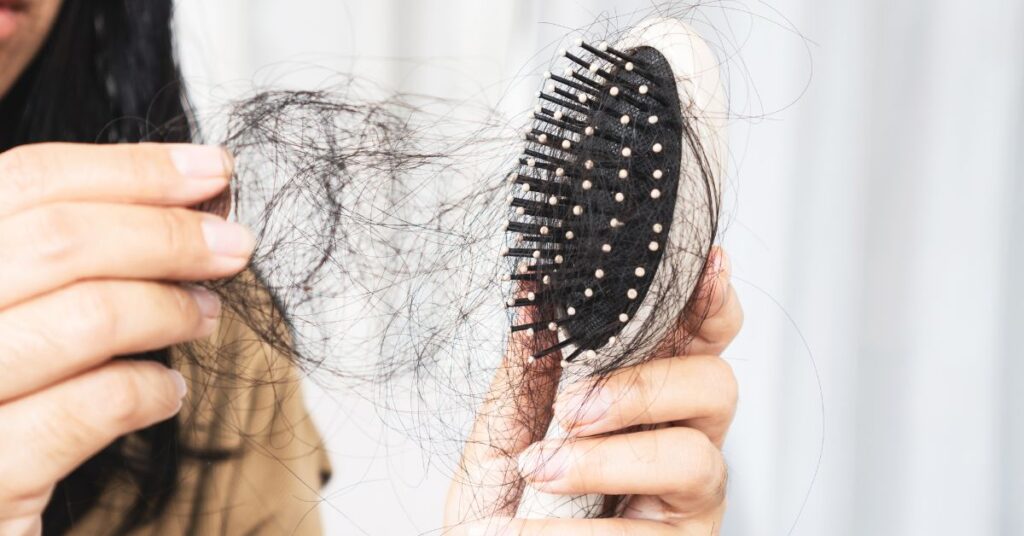

Introduce
Hair loss in women is a common yet often misunderstood phenomenon. While it’s natural for some hair to fall out regularly, excessive hair loss can be distressing. Understanding the causes behind hair loss is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. In this article, we delve into the various factors that contribute to hair loss in women, from hormonal changes to genetic predispositions and lifestyle influences. By gaining insight into these factors, you’ll be better equipped to address hair loss concerns and maintain healthy, vibrant hair.
Understanding Normal Hair Growth
Hair growth is a dynamic process that goes through distinct phases, each essential for maintaining a healthy hair cycle. Understanding these phases is fundamental to grasping the concept of normal hair growth and recognizing deviations that may indicate hair loss issues.
- Anagen Phase: This is the active growth phase of hair follicles, where cells in the hair root divide rapidly, leading to new hair formation. The duration of the anagen phase varies from person to person and can last anywhere from two to seven years.
- Catagen Phase: Following the anagen phase, hair follicles enter the catagen phase, a transitional stage where hair growth stops. This phase lasts for about two to three weeks, during which the hair detaches from the blood supply and becomes a club hair.
- Telogen Phase: The telogen phase is the resting phase of the hair follicle, lasting approximately three to four months. During this phase, the old hair is shed, making room for new hair growth. It’s normal to shed around 50 to 100 hairs per day during this phase.
- Exogen Phase: Some sources consider the exogen phase as part of the telogen phase, while others treat it as a distinct phase. It involves the shedding of the club hair that was formed during the catagen phase, allowing new hair to grow.
Factors such as age, genetics, hormonal changes, and overall health can influence the duration and effectiveness of each phase. Understanding the normal hair growth cycle provides a baseline for assessing hair health and identifying abnormalities that may signal underlying issues leading to hair loss.
Common Causes of Hair Loss in Women
Hair loss in women can result from a variety of factors, ranging from hormonal imbalances to genetic predispositions and medical conditions. Understanding these common causes is essential for effectively addressing hair loss concerns and implementing appropriate treatment strategies.
- Hormonal Changes and Imbalances:
- Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause, can contribute to hair loss in women.
- Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to hair thinning or loss.
- Genetic Predisposition:
- Family history plays a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to hair loss.
- Genetic predispositions to conditions like female pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) can result in progressive thinning of the hair over time.
- Medical Conditions and Treatments:
- Certain medical conditions and their treatments can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Autoimmune diseases, such as alopecia areata, can lead to sudden, patchy hair loss, while cancer treatments like chemotherapy can cause widespread hair shedding.
- Stress and Trauma:
- Psychological stress, physical trauma, or sudden weight loss can trigger a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium.
- This condition disrupts the hair growth cycle, leading to increased shedding of hair in its resting phase.
- Diet and Nutrition:
- Poor nutrition, deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals (e.g., iron, zinc, biotin), and crash dieting can impact hair health and contribute to hair loss.
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients essential for hair growth can help prevent nutritional-related hair loss.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Habits such as excessive hairstyling, frequent use of heat styling tools, and tight hairstyles (e.g., ponytails, braids) can damage the hair shaft and contribute to hair breakage and loss.
- Environmental factors like exposure to pollutants, UV radiation, and harsh chemicals can also compromise hair health.
Hormonal Influences on Hair Loss
Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact hair growth and contribute to hair loss in women. Understanding the role of hormones in regulating the hair growth cycle is essential for identifying and addressing hormonal-related hair loss issues.
- Role of Hormones in Hair Growth:
- Hormones play a crucial role in regulating the hair growth cycle by influencing the duration and activity of each phase.
- Androgens, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), can affect hair follicles’ sensitivity and lead to miniaturization of hair follicles in certain areas, particularly in female pattern hair loss.
- Hormonal Fluctuations During Life Stages:
- Puberty: Hormonal changes during puberty can affect hair growth patterns, leading to increased shedding or changes in hair texture.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy hormones, particularly elevated estrogen levels, can prolong the anagen phase of the hair growth cycle, resulting in thicker, fuller hair. However, postpartum hormonal fluctuations can lead to temporary hair shedding known as telogen effluvium.
- Menopause: Declining estrogen levels during menopause can contribute to hair thinning and loss, as estrogen helps maintain hair growth and thickness.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
- PCOS is a hormonal disorder characterized by elevated androgen levels, insulin resistance, and ovarian cysts.
- Excess androgens in PCOS can lead to symptoms such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth on the face and body) and male-pattern hair loss in women.
- Thyroid Disorders:
- Thyroid hormones, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), play a crucial role in regulating metabolism and energy production.
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can disrupt the hair growth cycle and lead to hair thinning and loss.
- Other Hormonal Factors:
- Hormonal contraceptives: Some hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills containing androgenic progestins, can contribute to hair loss in susceptible individuals.
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT): Estrogen and progesterone supplementation in menopausal women can influence hair growth patterns, but the effects may vary depending on individual hormone levels and formulations.

Genetic Factors and Hair Loss
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to hair loss, particularly in conditions like female pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia). Understanding the genetic factors underlying hair loss can help identify potential risk factors and guide treatment approaches.
- Female Pattern Hair Loss (Androgenetic Alopecia):
- Female pattern hair loss is the most common type of hair loss in women, characterized by progressive thinning of the hair, primarily in a pattern resembling male pattern baldness.
- Genetics plays a key role in androgenetic alopecia, with hereditary factors contributing to increased sensitivity of hair follicles to androgens like dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
- The inheritance pattern of androgenetic alopecia is complex, involving multiple genetic factors from both maternal and paternal lineages.
- Family History:
- A strong family history of hair loss, particularly among female relatives (e.g., mother, sisters), increases the likelihood of developing female pattern hair loss.
- Patterns of hair loss in family members can provide valuable clues about an individual’s genetic predisposition to hair loss.
- Genetic Markers and Risk Assessment:
- Genetic studies have identified specific genetic markers associated with an increased risk of developing female pattern hair loss.
- Genetic testing or analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) related to hair loss susceptibility may help assess an individual’s genetic risk profile.
- Other Genetic Conditions:
- In addition to female pattern hair loss, certain genetic conditions can contribute to hair loss in women.
- For example, conditions like alopecia areata and trichotillomania have genetic components that influence susceptibility to these disorders.
- Epigenetic Factors:
- Epigenetic modifications, such as changes in gene expression without alterations to the underlying DNA sequence, can also influence hair growth and loss.
- Environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and hormonal fluctuations can interact with genetic predispositions to modulate gene expression related to hair growth.
Medical Conditions and Treatments
Certain medical conditions and treatments can contribute to hair loss in women, either as a direct symptom or as a side effect of therapy. Understanding the potential impact of these factors on hair health is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management of hair loss.
- Autoimmune Diseases:
- Autoimmune conditions affecting the hair follicles can lead to hair loss in women.
- Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder characterized by patchy hair loss, resulting from the body’s immune system mistakenly attacking the hair follicles.
- Other autoimmune diseases, such as lupus erythematosus, can also cause hair loss as a secondary symptom of systemic inflammation.
- Hormonal Treatments:
- Hormonal treatments, including certain contraceptive pills and hormone replacement therapy (HRT), can influence hair growth patterns in women.
- Some contraceptive pills containing androgenic progestins may exacerbate hair loss in susceptible individuals, while HRT regimens can have variable effects on hair health depending on hormone formulations and individual hormone levels.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy:
- Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Chemotherapy drugs target rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles, leading to temporary hair loss known as chemotherapy-induced alopecia.
- Hair loss typically occurs within a few weeks of starting treatment and may continue throughout the course of chemotherapy.
- Medications:
- Various medications used to treat medical conditions can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Examples include anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, antidepressants, beta-blockers, and immunosuppressants.
- The mechanism of medication-induced hair loss varies depending on the specific drug but may involve disruption of the hair growth cycle or damage to hair follicles.
- Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Nutritional deficiencies, particularly of essential vitamins and minerals, can impact hair health and contribute to hair loss.
- Deficiencies in nutrients such as iron, zinc, biotin, and vitamin D have been associated with hair thinning and shedding.
- Addressing underlying nutritional deficiencies through dietary changes or supplementation may help improve hair health and reduce hair loss.
- Scalp Conditions:
- Scalp conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, and fungal infections can cause inflammation and damage to the hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
- Treating underlying scalp conditions is essential for restoring hair growth and maintaining scalp health.
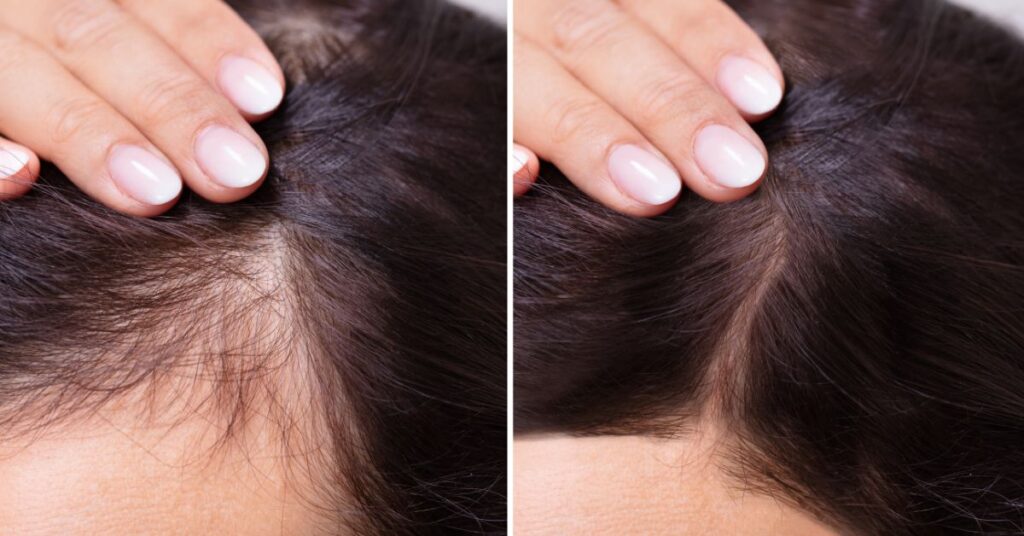
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the multifaceted nature of hair loss in women is essential for effectively addressing this common concern. From hormonal influences and genetic predispositions to medical conditions and treatments, various factors can contribute to hair thinning and loss. By recognizing the underlying causes and risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and mitigate hair loss, whether through lifestyle modifications, targeted treatments, or medical interventions. Additionally, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals can provide valuable support and expertise in navigating the complexities of hair loss and promoting healthy hair growth. With the right knowledge and strategies in place, women can empower themselves to maintain vibrant, resilient hair and preserve their overall well-being.read more
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) about Hair Loss in Women:
1. What are the main causes of hair loss in women?
- Hair loss in women can result from various factors, including hormonal changes (such as those occurring during pregnancy or menopause), genetic predispositions (such as female pattern hair loss), medical conditions (such as autoimmune diseases or thyroid disorders), certain medications or treatments (such as chemotherapy), and lifestyle factors (such as stress or nutritional deficiencies).
2. How can I determine if my hair loss is normal or if I should be concerned?
- While it’s normal to shed around 50 to 100 hairs per day as part of the natural hair growth cycle, excessive or sudden hair loss may indicate an underlying issue. If you notice significant thinning, patchy hair loss, or changes in hair texture, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist for evaluation and diagnosis.
3. Can hormonal imbalances contribute to hair loss in women?
- Yes, hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause, can influence hair growth patterns and contribute to hair loss. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders can also disrupt hormonal balance and lead to hair thinning or loss.
4. Are there any treatments available for hair loss in women?
- Treatment options for hair loss in women vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Medical interventions may include topical or oral medications, hormone therapy, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, or hair transplant surgery. Lifestyle modifications, such as stress management, dietary changes, and proper hair care practices, can also play a role in promoting hair growth and minimizing hair loss.
5. Can hair loss in women be prevented?
- While some causes of hair loss, such as genetic predispositions, may not be preventable, there are steps women can take to minimize the risk and promote healthy hair growth.

